Summary:
This blog explores the ethical considerations surrounding animal testing in the cosmetics industry. It examines the arguments for and against animal testing, the impact on animal welfare, and the growing movement towards cruelty-free practices. The post aims to provide a balanced view of the ethical debate and highlight the importance of finding humane alternatives.
Body:
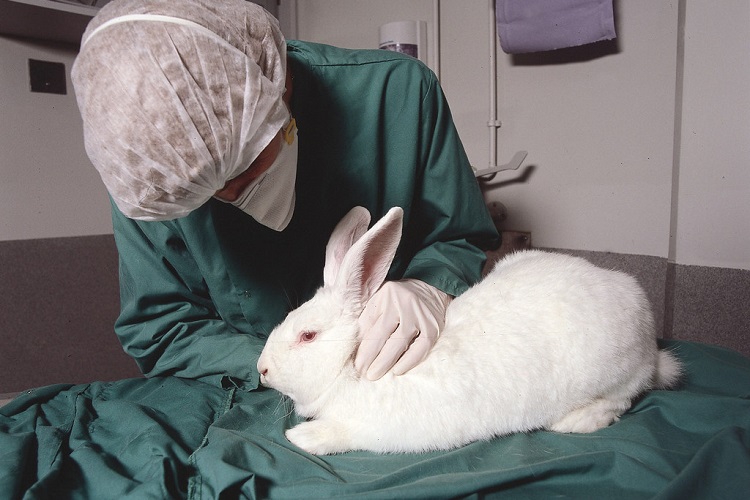
The ethical debate around animal testing in cosmetics is complex and multifaceted, involving a range of considerations about animal welfare, scientific necessity, and consumer safety. On one side of the debate are those who argue that animal testing is necessary to ensure the safety of cosmetic products for human use. They contend that without these tests, there would be a greater risk of harmful reactions and long-term health effects.
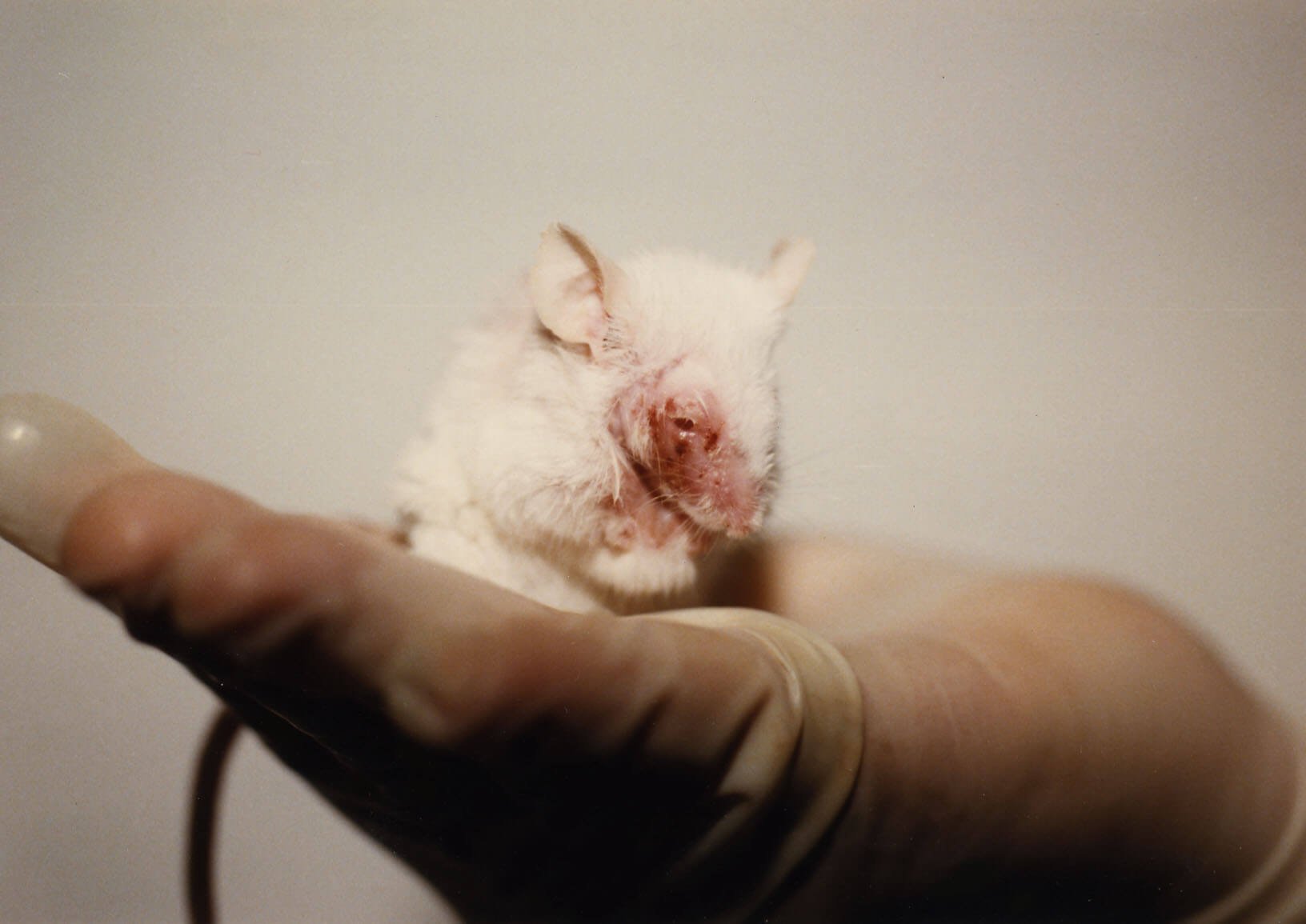
However, opponents of animal testing argue that the practice is inherently cruel and inhumane. Animals used in testing are subjected to significant pain and suffering, often resulting in long-term physical and psychological damage. Critics also point out that animals are often kept in small cages, deprived of social interaction, and subjected to repeated testing procedures, all of which contribute to their suffering.
Moreover, there is growing evidence that animal tests are not always reliable predictors of human reactions. Animals and humans often react differently to substances, making it difficult to extrapolate results from animal tests to human outcomes. This has led to calls for the development and adoption of alternative testing methods that do not involve animals.
The ethical debate is also influenced by cultural and societal values. In many Western countries, there is growing public opposition to animal testing, driven by increased awareness of the ethical issues involved. This has led to legislative changes, such as the European Union’s ban on animal-tested cosmetics, and the introduction of similar bans in other countries.
The movement towards cruelty-free cosmetics is gaining momentum, driven by consumer demand for ethical and sustainable products. Many companies are now adopting cruelty-free practices, using alternative testing methods such as in vitro testing and computer models. These methods are not only more humane but also often more cost-effective and reliable than traditional animal tests.
The ethical debate around animal testing in cosmetics is far from settled, but there is a growing consensus that alternative methods should be prioritized wherever possible. By supporting cruelty-free brands and advocating for legislative changes, consumers can help drive the industry towards more humane practices.
.jpg)